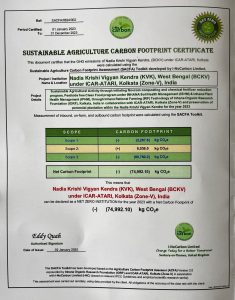
Nadia KVK Makes History as India’s First Net Zero Certified Agricultural Hub
Nadia Krishi Vigyan Kendra (BCKV), located in West Bengal under the jurisdiction of ICAR Agricultural Technology Application Research Institute (ICAR-ATARI), Kolkata, has made history by becoming India’s first net-zero certified Krishi Vigyan Kendra. Awarded the prestigious Sustainable Agriculture Carbon Footprint Certificate by UK-based certifying agency i-NoCarbon Limited, Nadia KVK has achieved a remarkable feat with a net carbon footprint of (-) 74.99 metric tonnes CO2e.
This achievement, driven by a MoU between ICAR-ATARI, Kolkata, and the Inhana Organic Research Foundation (IORF), Kolkata, pioneered India’s own carbon footprint assessment standard, leading to the development of ACFA Version 1.0—a tailored, Make-in-India carbon computing framework for diverse agro-ecosystems. Their partnership has not only set a new standard in sustainable agriculture but also paved the way for India’s own carbon footprint measurement standard in agriculture.
 |
 |
Recognizing the need for a tailored approach to carbon footprint assessment in agriculture, Indian scientists, in collaboration with various research institutes and organizations, developed the Agriculture Carbon Footprint Assessor (ACFA ver. 1.0). This comprehensive carbon computing standard considers India’s diverse agro-ecosystems and cultivation practices, embodying the spirit of
Make in India. ACFA ver. 1.0 integrates international frameworks such as the IPCC guidelines, GHG Protocol Agricultural Guidance, ISO 14064-1, and PAS 2050, while emphasizing a qualitative approach to agricultural management. A key feature is its two-value assessment, which evaluates the impact over different time horizons, ensuring a more realistic measurement of carbon footprints.
Building on this foundation, ACFA ver. 2.0 emerged as an enhanced and upgraded iteration, incorporating refinements for greater accuracy and applicability. A significant advancement from this was the development of the TEC Tool, based on ACFA ver. 2.0, designed not only to assess carbon footprints but also to raise awareness of sustainability footprints, particularly in alignment with the Regenerative Tea Initiative.
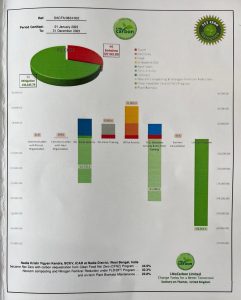
The assessment of Nadia KVK’s carbon footprint revealed key contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, including electricity consumption, livestock rearing, and on-farm activities. However, through sustainable agricultural practices and extension programs, Nadia KVK successfully mitigated these emissions.
The journey began with KVK’s sustainable intervention of the Clean Food Net Zero Model, implemented in collaboration with IORF, which emerged as a significant contributor to carbon mitigation. The MoU between ICAR-ATARI, Kolkata, and IORF further accelerated this initiative, driving innovation in sustainable agriculture and carbon footprint reduction. By promoting pesticide free and sustainable farming practices, coupled with the application of Novcom compost (a process developed by IORF), this initiative showcased remarkable results in reducing carbon emissions. In addition to on-farm activities, the preservation of trees and management of perennial horticultural plants within Nadia KVK’s premises contributed significantly to carbon sequestration. Altogether, these efforts resulted in a net carbon saving of 74.99 metric tonnes CO2e, highlighting Nadia KVK’s commitment to sustainable agriculture and environmental stewardship.
As India navigates the challenges of climate change, pioneering initiatives such as Nadia KVK’s Net Zero achievement and the development of ACFA ver. 1.0 and upgraded ACFA ver. 2.0 offer sustainable solutions for reducing carbon emissions in agriculture. The KVK Net Zero Model, integrated with the Clean Food Net Zero (CFNZ) Program, provides a transformative pathway for Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), Net Zero compliance, carbon credit generation, and soil restoration. This model, validated through the IBM-IORF Sustainability Accelerator Project, is a proven approach to carbon neutrality. With its adaptability to Voluntary carbon market (VCM) projects, aligned with India’s sustainability vision, it stands as a first-of-its-kind initiative, setting a global benchmark. Considering the 731 Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs) spread across the country, this initiative will help India move closer to a greener, more resilient future.
 |
 |
